Lesson- Control and coordination
Class-
10
1. What are plant hormones?
Ans- Plant
hormones or phytohormones are chemical substances which are produced naturally
in minute concentration in plants for regulating growth and other physiological
processes. These chemicals also bring about control and coordination in various
activities in plants. Important plant hormones are auxins, gibberellins,
cytokinins, etc.
2. How is the movement of leaves of a
‘Touch –me—not’ plant different from the movement of a shoot towards light?
Ans- The shoot of a plant responds to
light by bending towards it. It is a tropic movement. It happens very slowly
and this action involves growth. On the other hand, the leaves of sensitive
plants respond to touch (Shock) by folding up and drooping. It is a nastic
movement. This movement of leaves of sensitive plants does not involve growth.
Here, plant cells changes shape by changing the amount of water in the (turgor
changes).
Ans-
Auxins is responsible for promoting growth in plants.
3. How do auxins promote the growth of a
tendril around a support?
Ans-
Auxins are growth promoting hormones. The auxin moves from the side in contact
with the support towards the side of the tendril away from the support. As a
result, the side having more auxin growth faster than the side in contact with
the support. Hence, the tendril coils around the support.
4. Design an experiment to demonstrate
hydrotropism.
Ans- We
takes two glass troughs A and B and fills each one of them two- third with
soil. In trough A we plant a tiny seedling. In trough B we plant a similar
seedling and also place a small ‘clay plot ‘inside the soil. Water the soil in
trough A daily and uniformly. Do not water the soil in trough B but put some
water in the clay pot buried in the soil. Leave both the troughs for a few
days.
Now,
dig up the seedling carefully from both the troughs without damaging their
roots. We will find that the root of seedling in trough A is straight. On the
other hand, the root of seedling in trough B is found to be bent to the right
side (towards the clay pot containing water). This can be explained as follows.
In
trough A, the root of seedling gets water from both sides (because the soil is
watered uniformly).but in trough B, the root gets water oozing out from the
clay pot which is kept on the right side. So, the root of seedling in trough B
grows and bends towards the source of water to the right side. This experiment
show that the root of a plant grows towards water.
5. What is the difference between a
reflex action and walking?
Ans- Reflex
action is a spontaneous, automatic response to a stimulus on a specific receptor.
It occurs in a fraction of second and is mainly controlled by the spinal cord.
Reflex action does not require will of the organisms.
On the
other hand, walking is a voluntary action controlled by brain and occurs with
the will of the organisms. It takes longer time to react.
6. What happens at the synapse between
two neurons?
Ans- The
impulse receives by the dendrites of sensory neurons reaches the axon ending in
the form of an electric impulse. At the synape, it causes release of a chemical
neurotransmitter, acerylcholine(Ach)from synaptic vesicles in the synaptic
cleft. The neurotransmitter passes through the postsynaptic membrane in the
adjacent neuron and generates electric impulse. Thus, transmission of impulse
is an electrochemical phenomenon.
7. Which part of the brain helps
maintain equilibrium of the body?
Ans-
Cerebellum of the hindbrain.
8. How do we detect the smell of an
incense stick?
Ans-The
smell of incense stick stimulates olfactory receptor cells present in the
olfactory epithelium that lines the nasal chambers. The stimulus generates
electric impulse in the sensory cells and from here into the nerve fibers of
olfactory nerve. Thus, electric impulses from olfactory receptors are
transmitted through olfactory nerve to the olfactory lobes of forebrain. Here
these impulses are interpreted in the temporal lobe area of the cerebral
hemisphere.
9. What is the role of the brain in reflex
action?
Ans –
In several reflex actions brain acts like a relay centre which transfers
impulses from sensory to motor neurons. These are also called cerebral
reflexes. For examples, closure of eyes when exposes to bright light and
salivation at the sight or smell of tasty food. In spinal reflexes, brain may
act as an information collecting center.
10. How does chemical coordination take
place in animals?
Ans- In
animals, endocrine glands, when stimulated, release chemical substances called
hormones. These are directly poured into the blood which circulates them to all
the body tissue cells. Body tissue cells have specific molecules (receptors) to
identify specific hormones either on their surfaces or inside their cytoplasm.
Once the hormone combines with specific receptor present on target cells, it
then transmits the information to bring about the effect.
11. Why is the use of iodized salt
advisable?
Ans- Iodine
is essential for the synthesis of thyroxin hormone in the thyroid gland. The
thyroxin, in turn, regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism in the
body for growth. Deficiency of iodine results in goiter. Thus, use of iodized
salt is advisable to prevent iodine deficiency in the body.
12. How does our body respond when
adrenaline is secreted into the blood?
Ans- Adrenaline
is termed as emergency hormone. When a person faces stress or danger, it is
secreted in large amount to prepare the body to face emergency situations. It
increases the rate of heart beat and breathing, blood pressure, basal metabolic
rate and sugar level in blood.
13. Why are some patients of diabetics
treated by giving injections of insulin?
Ans- In
patients, suffering from diabetes, the blood sugar level is increased.
Therefore, the patient excretes sugar (glucose) in urine, feels excessive
thirst and also does excessive urination. Administration of injections of
insulin to them lowers the blood sugar level in them.
14. Which of the following is a plant hormone?
a.
Insulin b. Thyroxine c. Oestrogen d. Cytokinin
Ans-
Cytokinin
15. The gap between two neuron is called
a
a. dendrite
b. synapse c. axon d. impulse
Ans-
Synapse
16. The brain is responsible for
a. Thinking c. regulating
the heart beat
b. Balancing the body d. all of the above.
Ans-
all of the above
17. What is the function of receptors in
our body? Think of situations where receptors do not work property. What problems
are likely to arise?
Ans- The
receptor in our body collect information amount changes in the environment
around us in the form of stimuli. These then pass the information in the form
of nerve impulses to central nervous system (brain or spinal cord)where message
is interpreted and appropriate instructions are sent to effectors (muscles or
glands) which reveal responses. When receptors do not function normally, the
environmental stimuli are not able to create nerve impulses and body does not
respond.
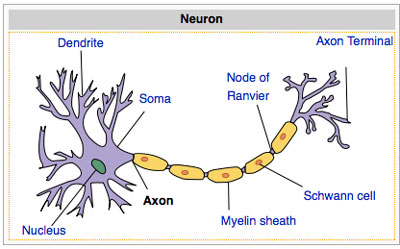
18. Draw the structure of a neuron and explain its function.
Ans- Neurons
present in the sense organs detect changes in the environment and transmit this
information to central nervous system which interprets the message and send
instructions via neurons to effectors for appropriate response.
19. How does phototropism occur in
plants?
Ans-Plant
is autotrophs, i.e., they manufacture their own foods in the presence of
sunlight. Therefore, they respond to light by growing towards it. Plants also
turn their leaves towards the sun to ensure that the latter get maximum sunlight.
This phenomenon can easily be depicted by performing simple experiment.
Take
two potted plants. Place one plant in the open so that it receives the
sunlight. Place the other plant in a room near the window in such a way that it
receives sunlight from one side only, i.e., through the window. After some
days, observe both the plants. You will notice that the first plant (which was
kept in the open) has grown up straight towards light. However, the second
plant (which was kept in the room and receiving light from one side) has grown
by bending towards the light.
20. Which signals will get disrupted in
case of a spinal cord injury?
Ans- In
case of spinal injury, reflex action and involuntary actions will get
disrupted.
21. How does chemical coordination occur
in plants?
Ans- In
plants, chemical coordination occurs with the help of plant hormones
(phytohormones). Specific hormones are secreted in one part of plant and these
diffuse to reach specific sites to produce the effect. The response of plants
to sunlight occurs by bending of the shoot towards it. It occurs due to slow
growth movements and the phenomenon is called positive phototropism.
22. What is the need for a system of
control and coordination in an organism?
Ans- In
multicellular animals, body is very complex. Therefore, it is necessary that
various organs (parts) of the body of an organism work together in a proper
manner to produce proper reaction to a stimulus. For proper control and
coordination, higher animals have evolved nervous system and endocrine system.
23. How are involuntary actions and
reflex actions different from each other?
Ans- Reflex
action are spontaneous, automatic, mechanical responses to specific stimuli
without the will of animal. In reflex actions, spinal cord is generally.
Involuntary actions also occur without the will of the animal and anima has no
choice in them. However, these are regulated by either midbrain of hind brain.
24. Compare and contrast nervous and
hormonal mechanisms for control and coordination in animals.
Ans-
s.no
|
Nervous information
|
Hormonal information
|
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
|
It is sent as an electrical impulse along axons, and as a
chemical across synapse.
Information travels rapidly, in milliseconds.
Information is directed to specific receptor- one or a few
nerve fibers, gland cells or other neurons. i.e, it is addressed by name.
It gets response immediately.
Its effect is short- lived.
|
1. it is sent as a chemical messenger
via blood stream.
2. Information travels slowly.
3.
Information is spread throughout the body by blood, from which the
target cells or organs pick it up, i.e., it is addressed to ‘whom it may
concern’.
4. It gets response usually slowly.
5. Its effects are generally more
prolonged.
|
25. What is the difference between the
manner in which movement in the sensitive plant and movement in our legs takes
place?
Ans- Sensitive
plant, in response to touch shows quick movement of leaves which fold up and
droop. Here, plant cells change shape by changing the amount of water in them (turgor
changes) affected by plant hormones. On the other hand, movement in our legs is
voluntary action which is controlled by cerebellum part of hind brain. It
involves nervous control.
No comments:
Post a Comment